Lost at home
Austrian Jewry and the US Consulate in Vienna

“Hundreds came in the belief that the United States was prepared to admit and to pay the passage of 20,000 immigrants. Consular authorities addressed groups of applicants, explaining the real situation.”
Vienna
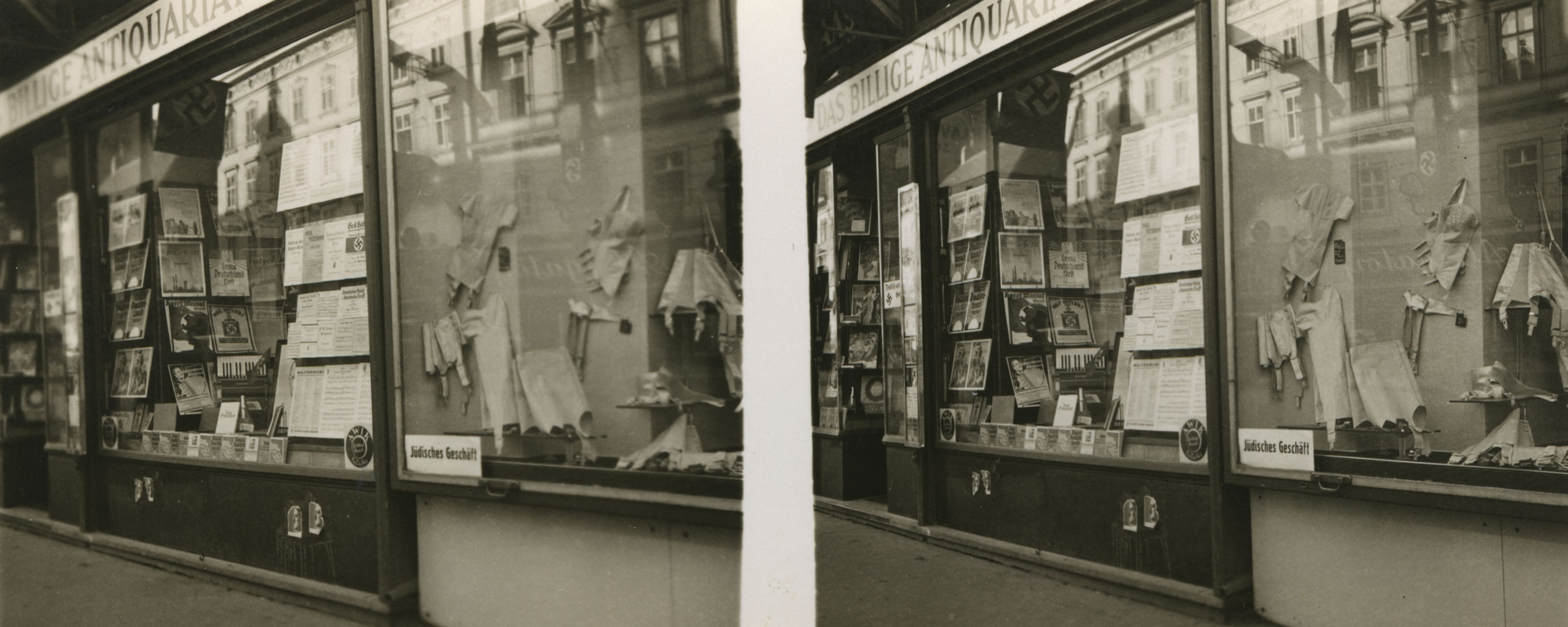
In another dramatic report from Vienna, the Jewish Telegraphic Agency describes panicked Jews flocking to the US Consulate hoping in vain to receive some kind of support. Especially prominent Jewish citizens faced harassment and arrest by the secret police. Austrian Jewish leaders were forced to inform the police about their activities, while their German counterparts were unable to come to their support due to border restrictions. The situation of thousands of Jewish actors had become so desperate that even the Nazi representative of the Austrian Theater Guild acknowledged it and permitted a campaign in their support.
SOURCE
Institution:
Collection:
“2,000 Jam U.S. Consulate at Vienna, Seek Visas” 
Source available in English
Chronology of major events in 1938
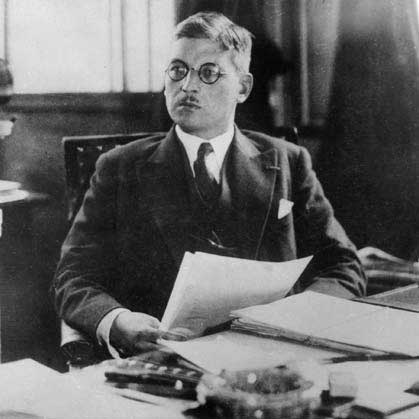
Roosevelt’s call for a conference on refugee crisis raises hopes

President Franklin Delano Roosevelt. Library of Congress.
In response to the dramatic rise in the number of refugees, US President Franklin D. Roosevelt calls for an international conference. Following the annexation of Austria by the German Reich on March 12, 1938, the number of people fleeing from the National Socialists rises significantly. By now, however, most countries have become unwilling to accept more refugees, placing victims of Nazi persecution in a desperate situation. Since 1933, two agencies under the auspices of the League of Nations—the Nansen International Office for Refugees and the High Commissioner for Refugees from Germany in Lucerne, have worked to solve the refugee crisis without success. The conference will convene July 6–15 at Évian-les-Bains, France.
View chronology of major events in 1938