The Jewish Hospital in Hamburg
Despite being undermined by the Nazis, the hospital keeps up its work

“As a friendly keepsake of our common years at the I.K.”
Hamburg
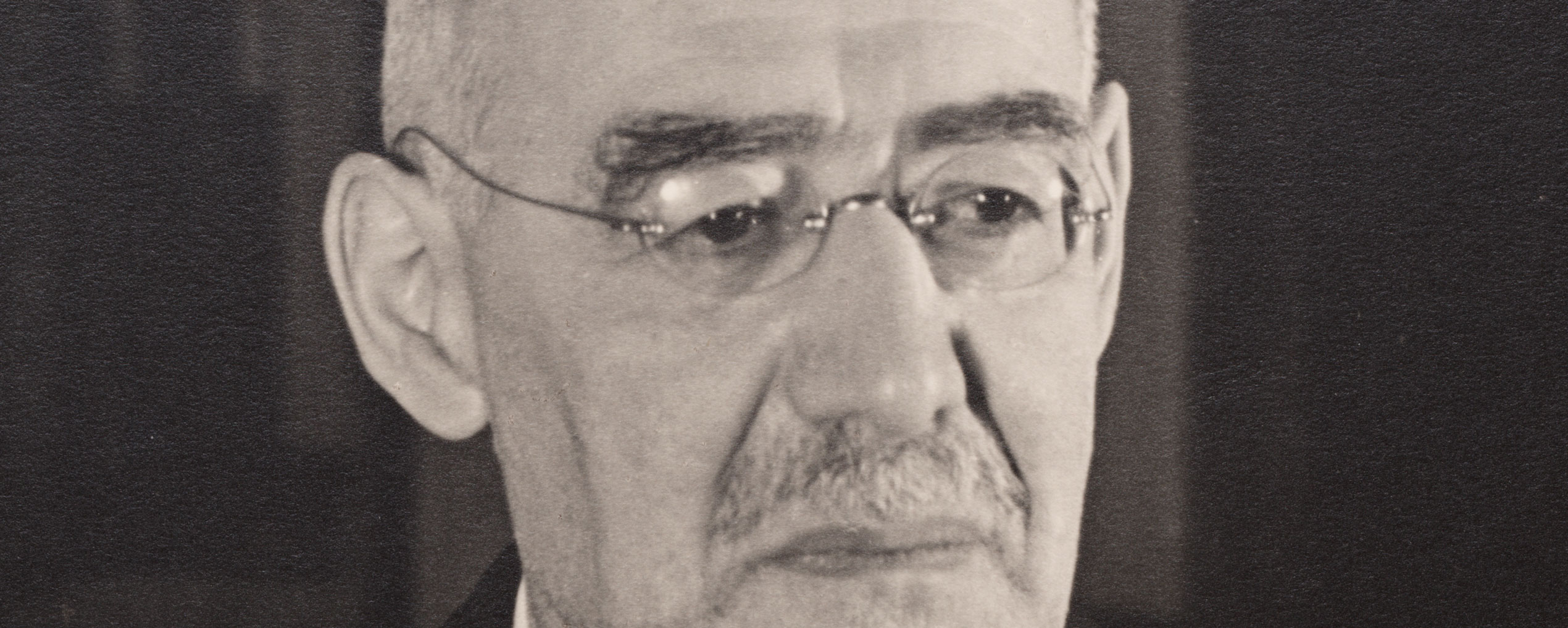
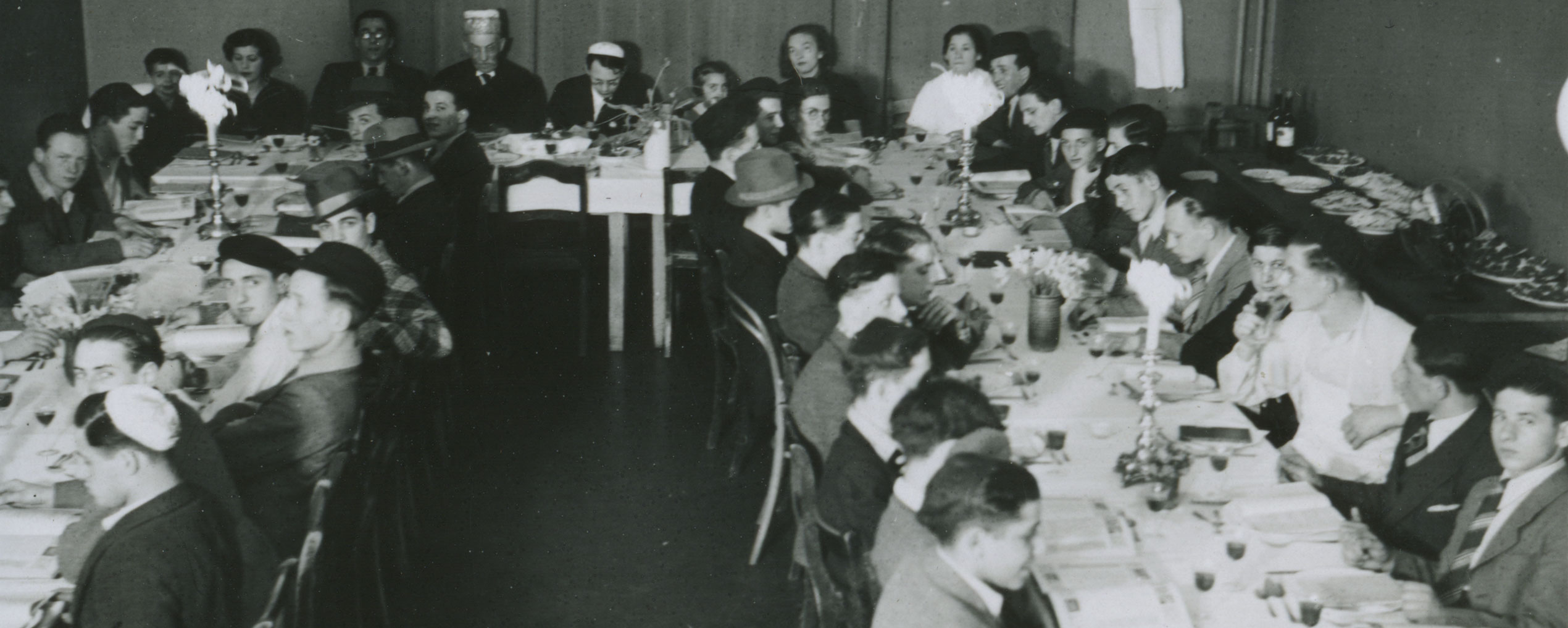
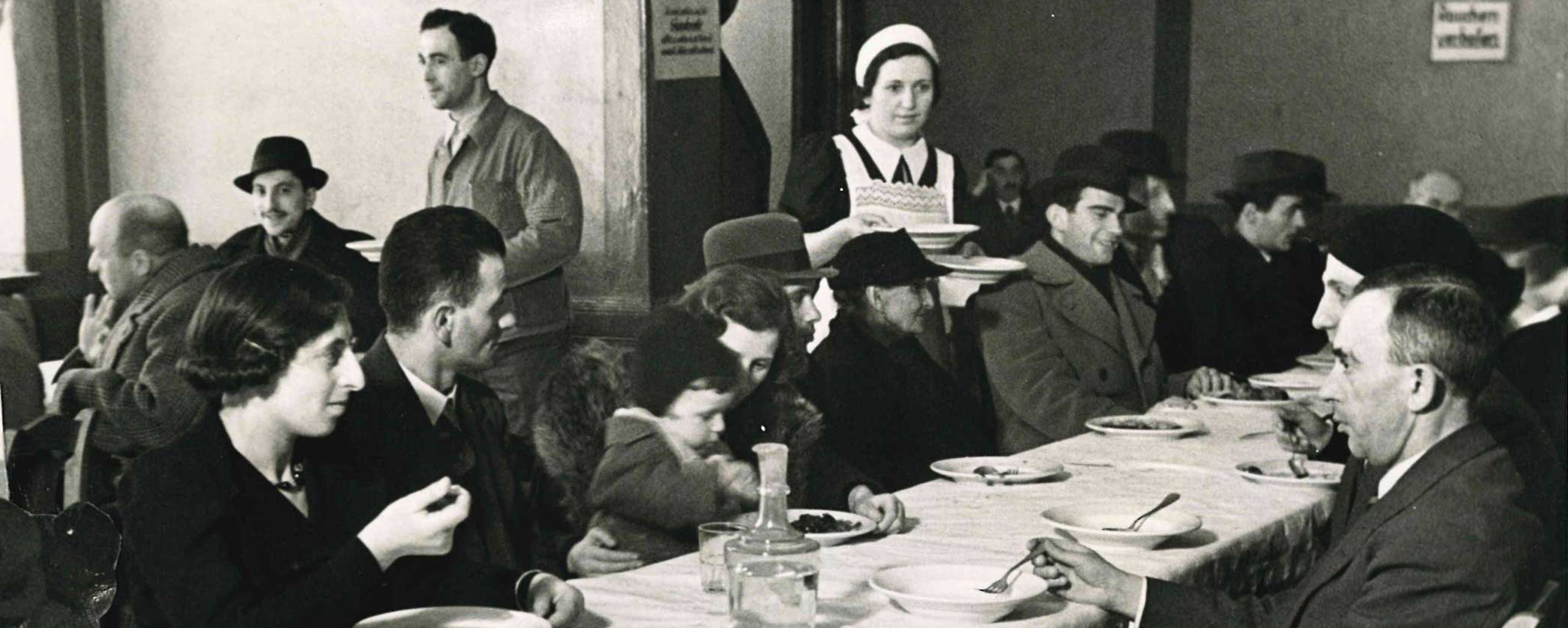
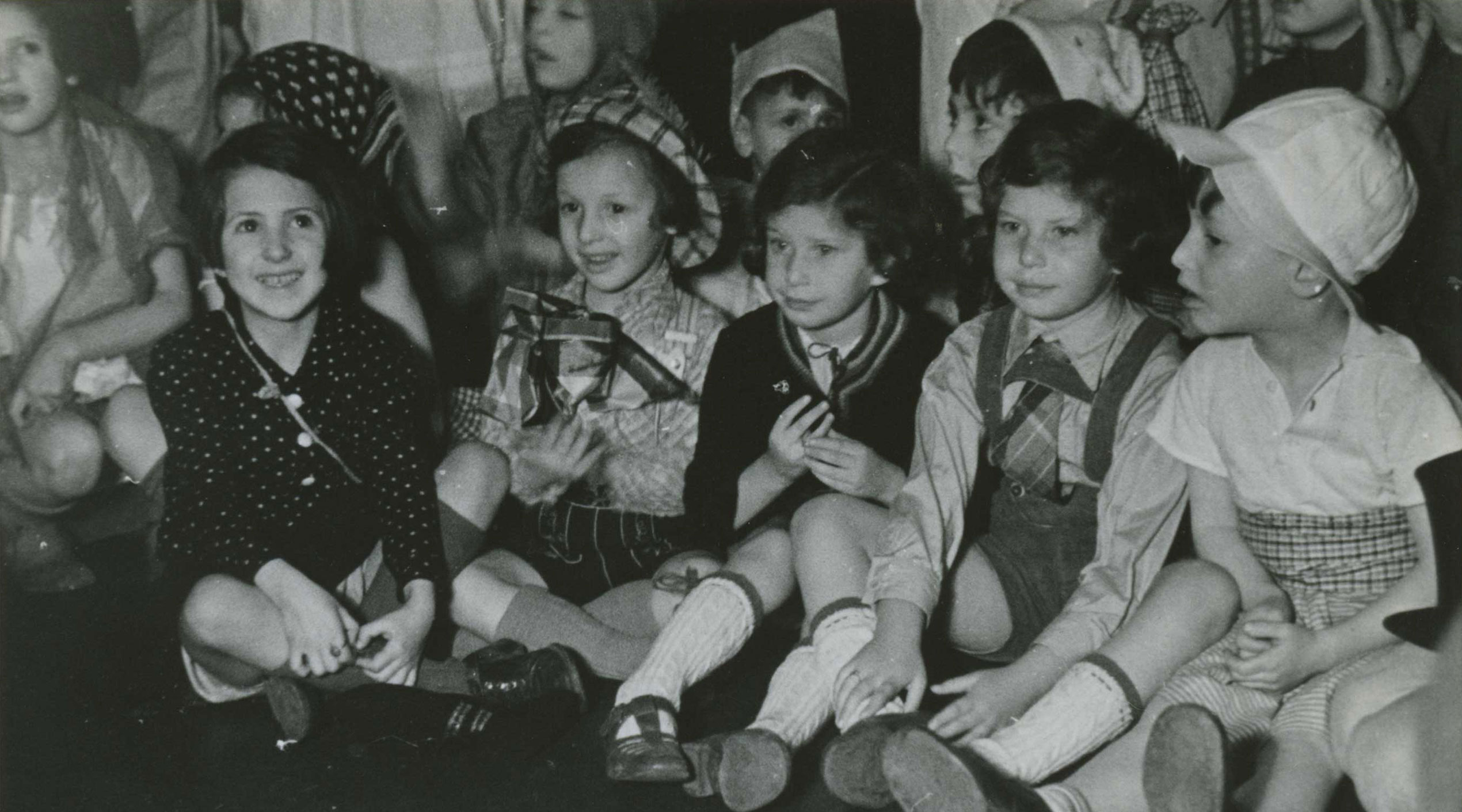
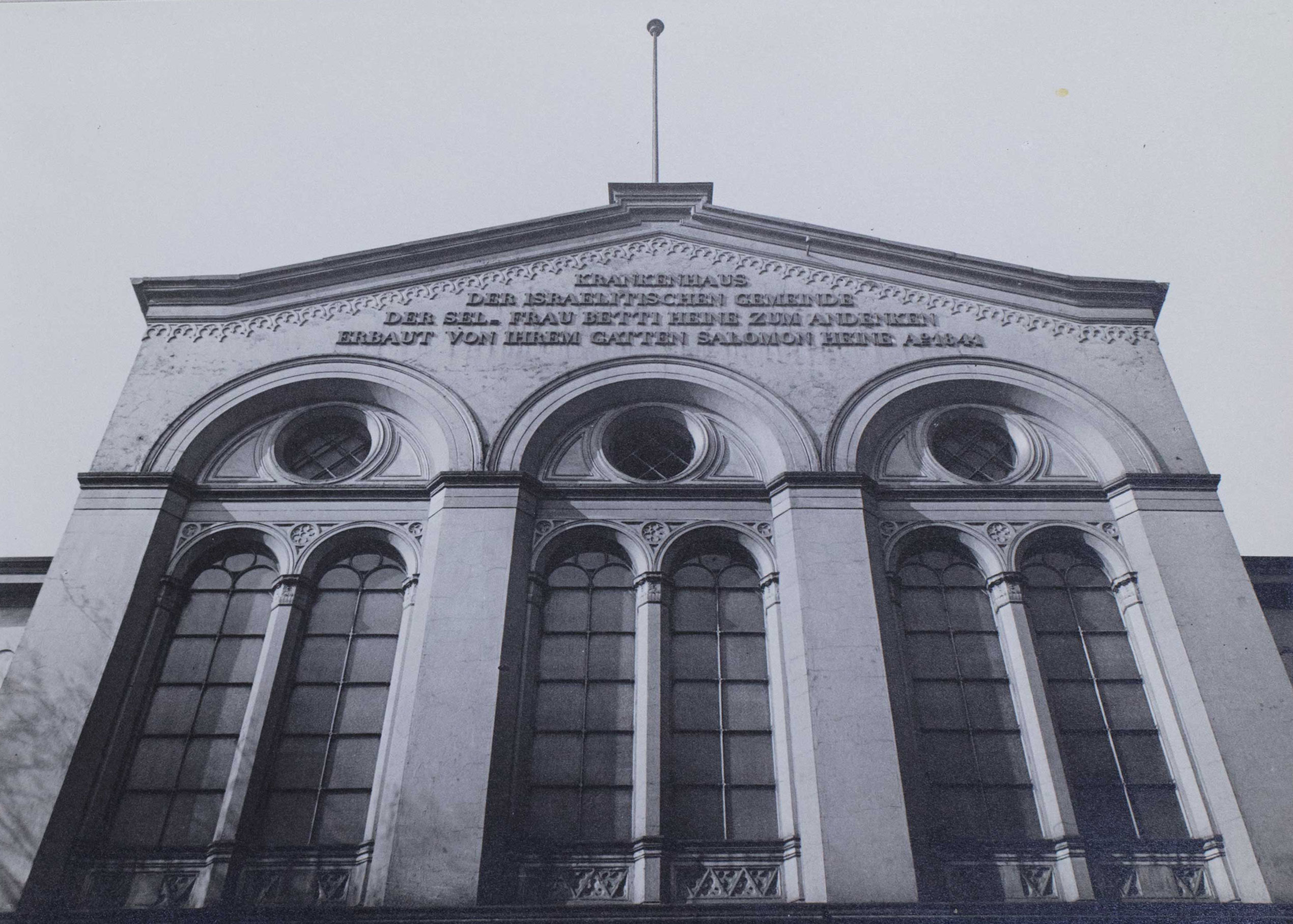
Depicted here is the facade of the Jewish Hospital in Hamburg. The photograph is part of an album preceded by the above inscription dated May 29, 1938. The hospital was endowed by merchant and banker Salomon Heine, also known as the “Rothschild of Hamburg,” in memory of his late wife Betty and inaugurated in 1843. The poet Heinrich Heine, Salomon’s nephew and beneficiary, honored the occasion with his poem Das neue israelitische Hospital zu Hamburg, in which he called it “A hospital for poor, sick Jews, for human beings who are thrice miserable, afflicted with three vicious ailments, with poverty, bodily pain, and Jewishness!” Even though the Nazi regime had been undermining the hospital’s finances since 1933, it had withstood these measures and was still able to take care of its patients in May 1938.
SOURCE
Institution:
Leo Baeck Institute – New York | Berlin 
Collection:
Israelitisches Krankenhaus, Hamburg, photograph album, AR 6812