Lifesaver
Frank Fenner from Michigan gives affidavit for nephew in Vienna

“...That I am willing and able to receive, maintain and support all those herein mentioned, and do hereby guarantee to save harmless the United States or any State, city or village or township thereof against any aliens herein mentioned becoming a public charge.”
Mendon, Michigan
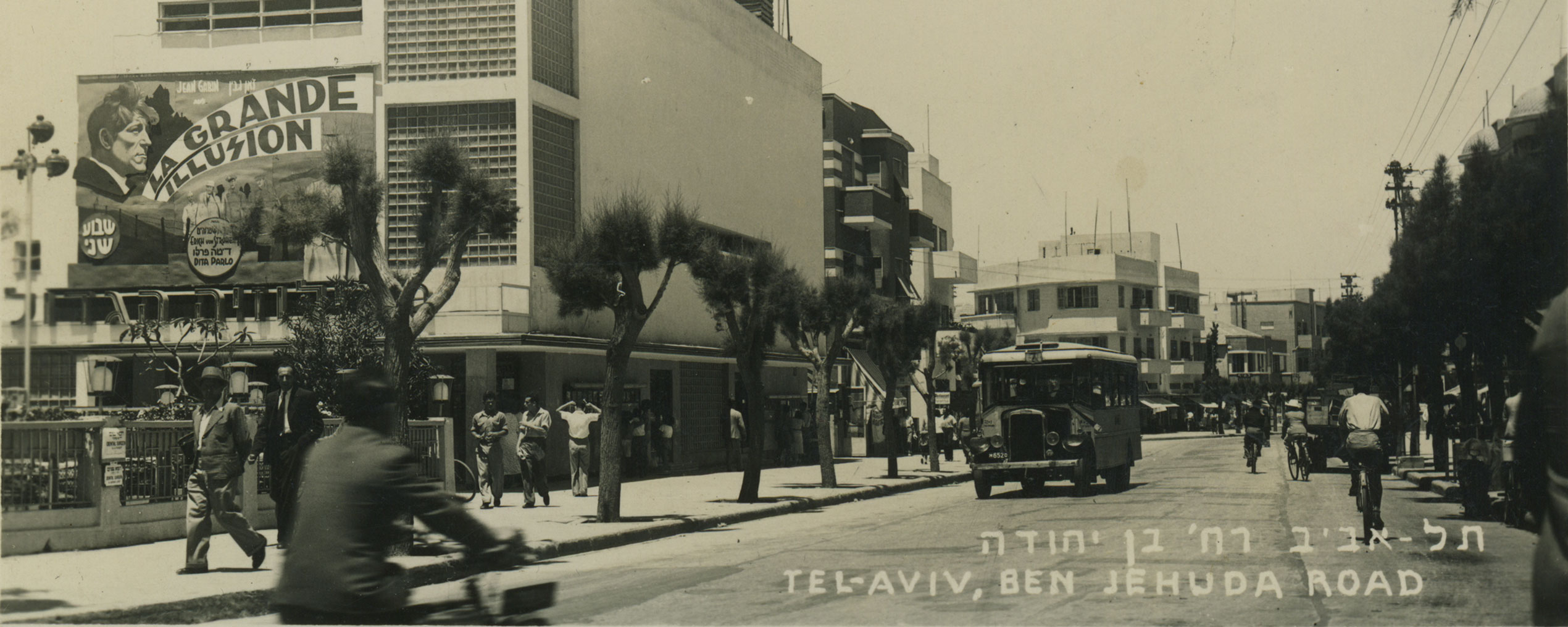
Close to 50 years before issuing an affidavit of support for his nephew, Karl Grosser, in Vienna, Frank W. Fenner had himself immigrated to the United States from Europe. A restaurant and confectionery owner in Mendon, Michigan, he pledged to support his young relative until the 26-year-old became financially independent. Finding a sponsor was a key prerequisite for obtaining an immigration visa that was often hard to fulfill. The visa process began by registering with the nearest US consulate, at which point a number on the waiting list was assigned. The length of the list depended on the number of Jews from a given country allowed to enter the US according to the quota system that had been in place since 1924. Despite the severe refugee crisis, quotas were not raised in 1938. During the waiting period, applicants had to procure all the required documents as well as certified copies. Prospective immigrants were lucky if their documents were still valid when their numbers came up.
SOURCE
Institution:
Leo Baeck Institute – New York | Berlin 
Collection:
Carl A. Grosser Collection, AR 10559 
Original:
Box 1, folder 1